Henan Liyue New Energy Co., Ltd

48V vs 51.2V Lithium Battery: Understanding Nominal vs Rated Voltage
When selecting a lithium battery for your energy storage system, electric vehicle, or industrial equipment, you’ve likely encountered a puzzling choice: should you choose a “48V” or a “51.2V” battery? This isn’t a marketing trick – it’s the key to understanding your battery’s core technology. In this article, we’ll demystify nominal voltage versus rated voltage, using lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) and ternary lithium batteries as examples to clarify this essential specification.
A Common Point of Confusion
Searching for lithium batteries often leads to a confusing scenario. You might ask yourself:
- Is it a “12V lithium battery” or a “12.8V lithium battery“?
- Should I choose a “24V lithium battery” or a “25.6V lithium battery“?
- What’s the real difference between a “48V lithium battery” and a “51.2V lithium battery“?
- Is a “72V lithium battery” the same as a “76.8V lithium battery“?
This isn’t an error or misrepresentation. On the contrary, precise voltage labeling is a sign of manufacturer professionalism. Let’s explore the critical technical reasons behind this seemingly small voltage difference.

I. Concept Analysis: Nominal Voltage vs. Rated Voltage
1. Nominal Voltage
Definition: The term “nominal” means “in name.” It’s an approximate voltage value used for easy classification and communication. It represents the average or expected voltage of a battery pack under standard operating conditions.
In the battery industry, we use terms like “12V system,” “24V system,” or “48V system” for simplicity. These nominal voltages help quickly identify the system’s voltage class, making it easier to select compatible equipment.
2. Rated Voltage
Definition: This is a more precise technical specification. It refers to the standard operating voltage of a battery under specific conditions, typically when fully charged. This value is directly determined by the battery cell’s chemical composition and the number of cells connected in series.
II. Calculating Your Lithium Battery’s Rated Voltage
The rated voltage stems from the fundamental technology of lithium batteries – the cell chemistry. A single lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) cell has a rated voltage of 3.2V, while a ternary lithium cell is rated at 3.7V.
You can calculate a battery pack’s total rated voltage with a simple formula: Rated Voltage = Number of Cells in Series × Voltage of a Single Cell.
Let’s examine the most common lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery:
- For a “12V system”: 4 cells in series × 3.2V/cell = 12.8V
- For a “24V system”: 8 cells in series × 3.2V/cell = 25.6V
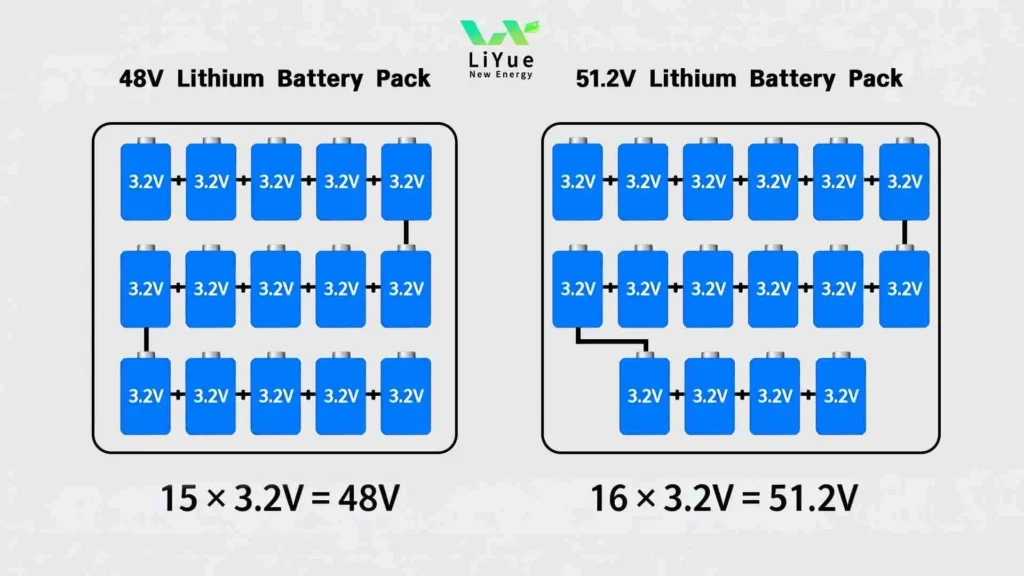
- For a “48V system”: 16 cells in series × 3.2V/cell = 51.2V
- For a “72V system”: 24 cells in series × 3.2V/cell = 76.8V
Therefore, a label of 51.2V instantly identifies a LiFePO4 battery with 16 cells. This is its precise technical designation.
For comparison, let’s look at Ternary Lithium batteries:
- For a “12V system”: 3 cells in series × 3.7V/cell = 11.1V (Often marketed as 12V)
- For a “48V system”: 13 cells in series × 3.7V/cell = 48.1V (Often marketed as 48V)
III. Why Do We Still Use Nominal Voltage?
We use nominal voltages like 12V, 24V, and 48V primarily for system compatibility and market conventions.
- Backward Compatibility: Most electrical systems and devices (like chargers, inverters, and motor controllers) were originally designed for lead-acid battery voltage levels. The average voltage of a lead-acid battery is close to these nominal values. For instance, a charged 12V lead-acid battery sits around 12.6V-12.8V, but we still call it a 12V system.
- Communication Ease: Using a round number like “48V” is far simpler for sales, marketing, and daily conversation than “51.2V” or “48.1V.” It defines a voltage platform, not an exact moment-to-moment value.
Trust Professional Labeling and Pay Attention to Details
When you see precise ratings like 12.8V, 25.6V, or 51.2V, you can trust the brand’s expertise. This transparency shows the manufacturer is accurately conveying the product’s true technical specs.
- Nominal Voltage (e.g., 48V) = The Common Name for easy communication and system compatibility.
- Rated Voltage (e.g., 51.2V) = The Technical Passport that reveals the battery’s chemistry and exact performance characteristics.
Before purchasing, always confirm the system voltage level (nominal voltage) your equipment requires. Then, check the product’s rated voltage to ensure a perfect match. This careful selection will result in safer, more efficient, and longer-lasting performance for your equipment.
夸大参数_-3D立体字效,_8000-CYCLES_(50撕毁)、_0--768x432.jpg)




